The convergence of factors such as the shift to hybrid work, the widespread use of digital communications and mobile devices, and the proliferation of unsecured messaging and collaboration tools has elevated secure and compliant business communications to an indispensable requirement for organizations across diverse sectors. Several security and compliance gaps can be traced to unsecured business communications; in addition to increased exposure to cyberattacks, these vulnerabilities raise the risk of noncompliance with industry regulation. Here we draw insight from various Workforce Productivity & Collaboration and Information Security surveys illustrating how market requirements for business communications are evolving in response to changing work dynamics and emerging cybersecurity threats.
The Take
Traditionally viewed as niche solutions tailored for specific industries, the relevance of secure and compliant workplace messaging and collaboration technologies is changing. In many cases, adoption has been triggered by cyberattacks and direct actions from regulatory bodies. However, our research shows organizations are increasingly recognizing the critical nature of these technologies and the need for a proactive, rather than reactive, approach. This signals an impending shift from early to late majority adopters for secure and compliant collaboration and communications technology in 2024.
Secure and compliant communications are critical for hybrid work
Nearly two years since COVID-19 lockdown restrictions were phased out, 49% of respondents to our Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Digital Transformation 2023 survey of enterprise IT decision-makers say they expect a majority of desk workers in their organization will be working remotely full time (23%) or have a hybrid schedule (26%) a year from now. These numbers are very similar to data from our Workforce Productivity & Collaboration Technology Ecosystems 2022 and 2021 surveys, indicating the pandemic resulted in permanent changes in the workplace.
Survey results show the top challenges for supporting a more distributed workforce over the next two years cited by respondents include employee retention (39%), keeping employees focused and aligned (37%), privacy, security and compliance (36%), and team building (36%). Notably, survey data shows that those respondents working for organizations identified as digital transformation leaders (i.e., those that have a formal digital transformation strategy and are actively digitizing business processes and technologies) are significantly more likely to identify privacy, security and compliance as the top challenge for supporting a more distributed workforce.
Employee use of use of digital communications and mobile devices
Our research shows employees rely extensively on a range of communications tools in the workplace, including personal devices and consumer messaging services. While not a recent trend, the threat landscape has changed over the past two years, significantly raising the risk level. This includes emerging threats such as “smishing” — a portmanteau of short-messaging service (SMS) and phishing — a form of social engineering attack that relies on fake text messages to trick people into downloading malware, sharing sensitive information or sending money to cybercriminals. Furthermore, generative AI has emerged as a looming threat, given that it could potentially be used to create malware and evade detection.
Our Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Work Execution Goals & Challenges 2023 survey shows the following usage patterns for mobile devices and messaging applications in the workplace:
- Two of three organizations allow the use of personal devices. One of three (32%) respondents say their employer allows access to any company system on their personal device, while an additional 36% say their employer allows access only to specific work applications.
- Nearly three of four employees use their smartphone on a daily basis. More than half (53%) of survey respondents use their smartphone for business purposes several times a day, while an additional 20% say they use it once a day. The top applications used are voice calls (67%), email (64%) and messaging (57%).
- The use of personal devices is expanding beyond smartphones. A significant number of respondents use personal devices other than a smartphone for business purposes, including laptop computer (83%), tablet (48%) and wearable device (38%).
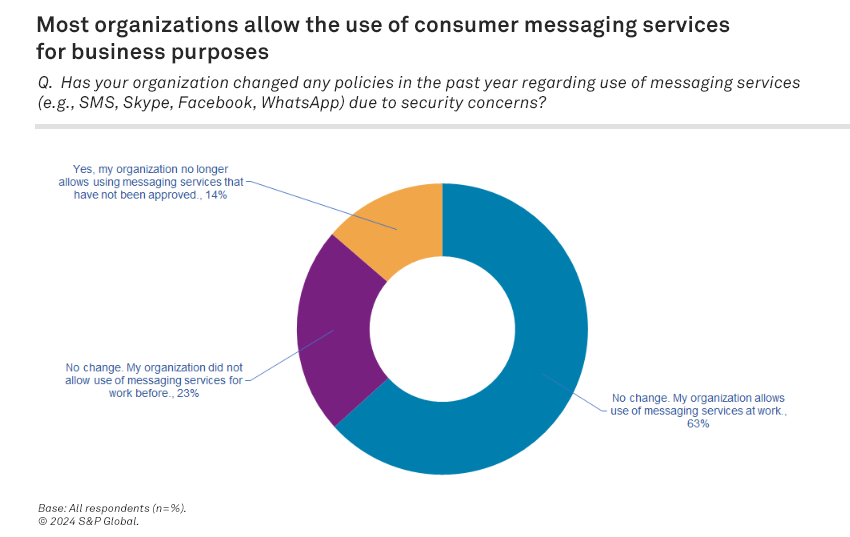
- Nearly two of three organizations allow the use of consumer messaging services. When asked if their organization had changed any policies in the past year regarding the use of consumer messaging services such as SMS, Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp due to security concerns, 63% of respondents said their organization still allows their use at work.
Pressure to comply with industry regulation is intensifying
Actions taken by the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) over the past two years signal increased scrutiny of electronic communications recordkeeping compliance by financial firms and banks. In September, US regulators fined eight companies a combined $111 million over record-keeping lapses — the latest in a series of enforcement actions levied over financial firms and major Wall Street banks for “widespread and long-standing failures” to maintain and preserve work-related electronic communications. The SEC cited the use of WhatsApp, text messaging and personal email accounts by junior staff members and senior executives bypassing mechanisms designed to keep a record of business-related communications, in violation of recordkeeping provisions of the federal securities laws.
Organizations face emerging cybersecurity threats
The use of unmonitored communications leaves the door open to cyberattacks using text messages and phone calls that can lead to ransomware and crypto viral extortion. According to our Information Security, Endpoint Security 2023 study, this is top of mind for IT decision-makers. Survey results show 23% of participating respondents say their company had been a victim of ransomware in the previous 12 months, up from 18% of respondents to the previous year’s study.
Furthermore, the Strengthening American Cybersecurity Act of 2022 gives the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) the ability to subpoena critical infrastructure entities and federal civilian agencies to compel disclosure of cyber incidents. This entails the possibility for information to be made available to journalists via public records requests, highlighting the urgency for organizations to expand their cybersecurity initiatives and adopt a proactive approach, focusing their efforts on prevention and risk mitigation.
Secure and compliant communications are a “must have” requirement
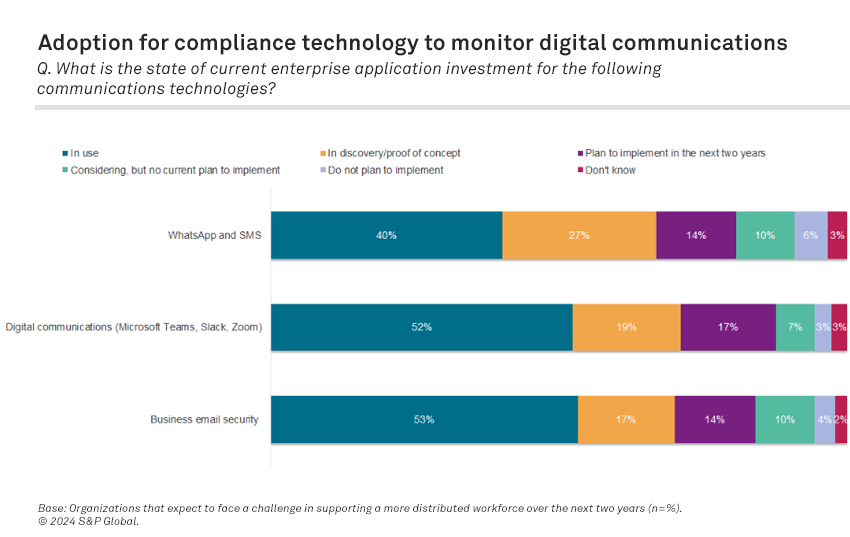
Although still lagging business email security, non-email digital communications are emerging as a critical enabling component for a distributed work environment. Our Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Digital Transformation 2023 survey shows that a majority of participating organizations have deployed — either in production or proof of concept — compliance technology to monitor and act on the content of non-email digital communications. This includes internal communications (i.e., team collaboration and video conferencing tools) at 71%, as well as external communication services such as WhatsApp and SMS, when used for customer engagement (67%), reflecting a growing awareness for secure and compliant business communications and collaboration.
Want insights on Infosec trends delivered to your inbox? Join the 451 Alliance.

