Generative AI has reframed the enterprise understanding of artificial intelligence, from a tool for pattern classification to an engine of content generation. This has reshaped the landscape for automation, opening up a wealth of opportunity in areas such as copy generation, product design, translation and summarization. The recent advancement in the field is perhaps less about technology — many of the more prominent model families have been in development for years — and more about productization and accessibility. However, the latter — greater accessibility — has created a virtuous cycle with the former — technological advancement — with rapidly growing user bases encouraging a wave of new investment.
The popularity of ChatGPT, released to the public as a research preview by OpenAI in November 2022 and achieving over one million users within a week, spawned an array of startups and kicked off a race by major technology providers to compete for mindshare. Progress has been so rapid that we have released a number of monthly digests: the first three are here, here and here. This report will explore and contextualize some of the insight from S&P Market Intelligence’s Generative AI Market Monitor, which assesses and forecasts revenue for over 260 companies offering generative AI products. The report looks at seven distinct media-generation segments: foundation models, alongside generators of text, images, audio, video, code and synthetic structured data.
The Take
Generative AI as a market is currently best understood in the context of distinct media-generation segments, underpinned by foundation models. Each segment demonstrates discrete market characteristics and competitive dynamics. These distinctions appear to be gradually eroding, with segments already coalescing. Early intersections are being seen between text and image generators, increasingly brought together when generating copy, and in the expansion of foundation models trained on code and text. The boundaries are blurring not just between segments, but also the market definition itself, as generative AI models are increasingly integrated into other software products, in many instances servicing as an interface.
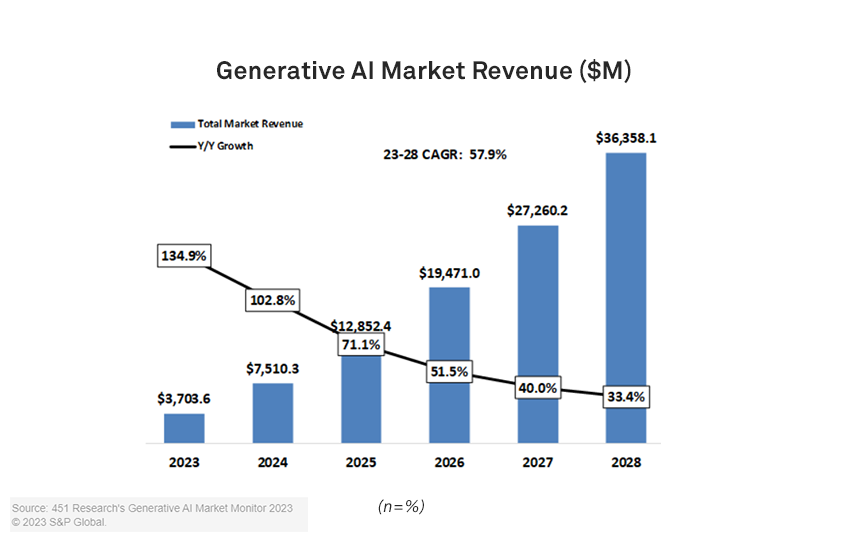
The forecast revenue growth for companies in these media-generation sectors is substantial — a 58% compound annual growth rate from 2023 to 2028. This reflects growing enterprise awareness of the opportunity, as well as the sector’s transition from research to monetization — a tendency well illustrated by OpenAI’s commercial redirection. The wide array of use cases that generative AI capabilities can be applied to, as well as the evolution of the technology in an increasingly enterprise-friendly direction, makes for a strong foundation for ongoing growth.
Rapid growth, but not equally distributed
Generative AI revenue is expanding at pace, with aggregate revenue expected to rise from $3.7 billion in 2023 to $36 billion by 2028. As Figure 1 illustrates, growth rates show significant variability, with code generators primed for the fastest expansion (73% CAGR) and the text generators the least, at just under 50%. This, in part, reflects the relative maturity of the two markets.
The text-generator space is made up of a burgeoning ecosystem of software companies, many targeting sales and marketing use cases. A number of long-standing companies have been active in the space from early 2021, and have recently been joined by a wave of startup entrants, stimulated by lower-than-expected costs of large language model APIs. As the most competitive market of any segment assessed — the eight largest providers by revenue only make up 44% of the total market — the sector may begin to see some consolidation. The challenge for many text-generator startups is a lack of differentiation, not only from each other, but also from the evolving offerings of foundation model providers. The array of enterprise-targeted features, services and partnerships emerging from foundation model providers makes it increasingly difficult for text-generator startups to justify a position in the AI stack, with businesses able to engage with the largest model providers directly.
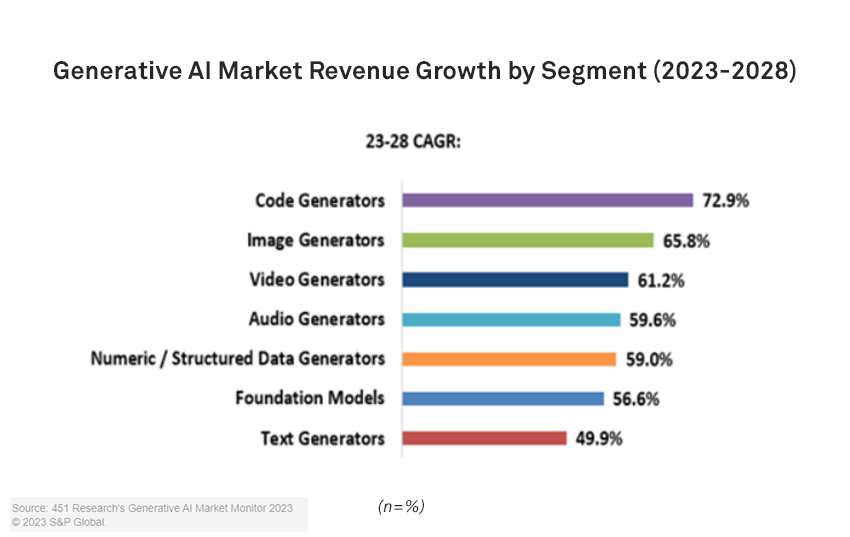
In comparison with the relatively well-established text-generator space, code generation remains relatively embryonic. The code-generation sector has significantly smaller forecast aggregate 2023 revenue than text generation: $231 million against $1.1 billion. While, in part, this likely reflects enterprise risk considerations — with the auto-generation of email templates requiring a lower risk appetite than contributing code snippets to a mission-critical application, for example — it also reflects recency, with highly performant code-generation tools only really emerging in recent months. As an illustration, Amazon CodeWhisperer was only made generally available in April — the month that saw Google Bard updated with code-generation features. These releases came only a few months after Stack Overflow banned the use of ChatGPT to answer user queries due to the poor quality of contributions.
The image-generation sector is also set to see substantial growth. Forecasts for 2023–2028 suggest an excess of 65% CAGR, and from a higher base than code generation at $426 million for 2023. This robust trajectory is driven, in part, by the entrance of established technology providers with large, curated image libraries. Adobe Inc.’s Firefly beta was announced in March, and the company has subsequently partnered with Google on text-to-image capabilities and integrated Firefly into Photoshop. Shutterstock currently offers a free Al image generator — a capability that is likely to be wrapped into its upcoming design assistant. Despite the entry of these players, the market is unlikely to consolidate too sharply. The top four companies are expected to generate around 38% of revenue by 2025 as more focused providers enter the space.
Structured data generation is an emerging area, and the smallest segment assessed in our Market Monitor. Much of the £135 million in forecast revenue for 2023 derives from a handful of well-capitalized startups. The relatively stable trajectory of the space — 126% growth in 2023 and 98% in 2024, despite starting from a low base — reflects that generative AI techniques are just one of several approaches to building artificial data sets. That said, growing concerns around data set privacy, and the opportunity for such techniques to retain patterns without exposing sensitive data, could help revenue growth exceed forecasts.
Enablers of growth
The breadth of use cases generative AI can be applied to will likely keep the market on a pronounced growth trajectory. Large language models, trained on huge volumes of data and with large parameter counts, perform well across a wide array of tasks, even where little use-case-specific data is available. Even with little tuning, text-generation capabilities can provide a valuable interface for many sales, customer and staff engagement tasks. Similarly, the most prominent image generators are highly generalized, trained on such a large corpus that a marketing department for a professional services company or a designer building an educational website can make use of the same tools. As enterprises and technology providers place greater emphasis on tuning — a transition that is already taking place — use cases requiring more specificity will be more commonly exposed to generative AI capabilities, whether technical document generation, prescriptive analytics tools or video advertising.
The ability to better support tuning is just one of a number of ways the market is transitioning to facilitate greater business adoption. Clearer and stronger positions on privacy, with few companies keen to have proprietary or sensitive data exposed to third parties, represent a notable shift in generative AI messaging. In addition, the market is already seeing a wide array of partnerships, connectors and integrations designed to ease the process of engaging with the technology. Combined with expanding professional services expertise, the wrapping of these models in developer tooling, and greater clarity in business policies, these drivers will likely expand revenue from the enterprise customer segment significantly within a short time frame. As Figure 1 illustrates, forecast growth rates for both 2023 and 2024 are in excess of 100%. The code and video sectors are forecast to exceed 150% over 2023.
Revenue growth may also be driven by price increases. Sizeable funding and an early race for market share appear to have repressed pricing. As markets consolidate — with the forecast market share of the top eight generative AI companies expected to shift from 66% in 2023 to 80% by 2028 — these dynamics are likely to change. As generative AI looks to emerge both as an increasingly critical and integrated aspect of many applications and as an interface between users and their software investments, demand for foundation model APIs is unlikely to be price sensitive. Cost and complication in switching, a challenge across many technology investments, may be worsened by the desire to fine-tune generative AI for many use cases. These conditions may lead to a generative AI market with strong supplier power, and consequently medium-term price inflation.
A number of technological enablers are also expanding the market, not just by increasing the viability of establishing new models, but also by laying the groundwork for enterprises to take advantage of them. Access to greater processing power, large-scale data storage and broader use of AI accelerators has opened the door to mainstream enterprise engagement. The ongoing expansion of the open web and the long-standing digital transformation shift of enterprises have created a robust training set for new models and enhanced the levels of specificity that can be achieved with fine-tuning.
Risks and inhibitors
Legal and regulatory concerns continue to swirl around generative AI, with data privacy and intellectual property two key focal areas. Global regulatory frameworks appear to be diverging, further complicating the ability to map impact. Regulatory proposals being drafted by the Cyberspace Administration of China suggest a strict framework is likely to be instigated — for example, where model providers can be held responsible for subversive content generated and users will need to be verified individuals. Conversely, the UK is setting out early growth-orientated objectives that indicate a highly liberal regulatory regime. The country has already introduced changes to ease regulation on text and data mining.
The evolution of legal and regulatory frameworks will influence not just the geographic makeup of startups operating in the space, limiting growth in some regions, but could also change global competitive dynamics in favor of larger providers. A lack of clarity may also prove challenging for startups. There have been some well-publicized cases filed against image-generator platforms in the US, including image licensing service Getty Images Holding Inc., alleging the improper use of its photo repository by Stable Diffusion. Small technology providers may feel less able to take risks in ingesting materials than better capitalized alternatives, creating a stratified market for models.
Another risk may emerge from a seeming disconnect between model capability, trust and measurement. Data from our AI & Machine Learning, Use Cases 2023 indicates that 94% of respondents view AI as important to their transformation efforts — roughly half of which see the technology as “very important.” However, only 52% of respondents were monitoring models for performance anomalies, and 66% “mostly” or “completely” trusted third-party AI predictions. Early enthusiasm for generative AI, and the risk of models providing inaccurate or unsuitable outputs, could lead to a situation where the overextension of these technologies, alongside monitoring gaps, could lead to negative outcomes and hold back future enterprise adoption.
Want insights on AI trends delivered to your inbox? Join the 451 Alliance.