
Source: 3alexd/Stock Photos | Electric Car/iStock by Getty images.
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum as organizations and consumers alike recognize the potential economic and environmental benefits. However, significant barriers remain that hinder widespread adoption. According to a study conducted by S&P Global Market Intelligence 451 Research, addressing these barriers to adoption is crucial for accelerating the adoption of an electric future.
Cost and infrastructure
Despite the enthusiasm for EVs, high retail prices and limited inadequate charging infrastructure are major barriers to adoption.
For non-EV owners, 36% cite high retail prices as a primary barrier, while 20% point to the lack of charging infrastructure.
The fear that an EV will run out of power before reaching its destination or a charging station, also known as range anxiety, and overall charging wait times contribute to consumer reluctance.
To overcome these barriers, automakers and policymakers must prioritize expanding charging networks, especially by strategically locating direct current (DC) fast-charging stations. Preferred charging locations include highway rest areas, urban areas, and everyday stops.
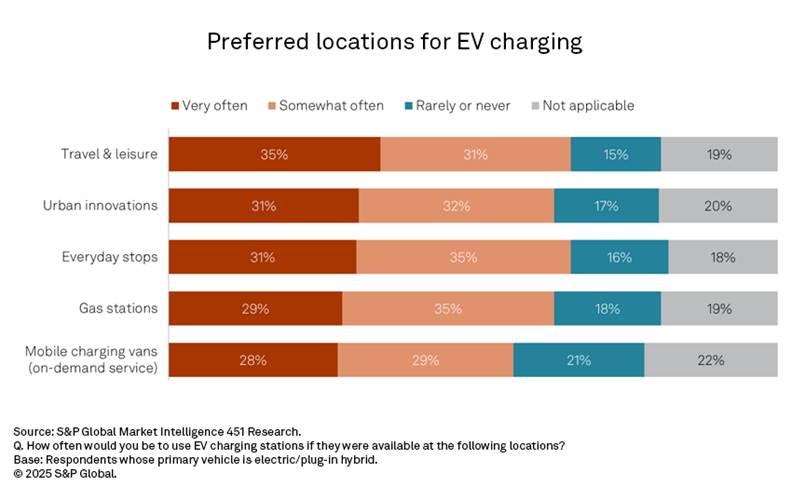
Additionally, transparent pricing and financial incentives can help make EVs more accessible by focusing on the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront cost.
Building trust in EV technology
Another critical barrier facing the automotive industry in the adoption of EV technology is the gap between overall technological readiness and consumer trust. Safety concerns, particularly regarding vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, hinder adoption. V2G technology allows EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also return electricity to it, offering cost savings and grid resilience. However, safety concerns such as fire risks and battery degradation create hesitation.
To build confidence, transparent communication, real-world use cases, and warranties covering V2G usage are essential. Establishing partnerships between utilities and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) can ensure V2G reliability and safety, positioning the first movers as leaders in this emerging market.
Addressing environmental skepticism
Despite the growing popularity of EVs, skepticism about their environmental benefits persists.
According to the survey conducted by S&P Global Market Intelligence 451 Research, only 43% of consumers view EVs as environmentally beneficial, with concerns about electricity sources, lifecycle emissions, and battery production contributing to the perception gap.
To address this, the automotive industry must shift its narrative from focusing solely on “zero tailpipe emissions” to a transparent discussion of the full lifecycle. This includes substantiating environmental claims with clear lifecycle assessments and promoting renewable energy integration for charging.
The role of public-private partnerships
Public-private partnerships can play a pivotal role in overcoming these barriers. By collaborating to electrify public transportation and develop robust charging infrastructure, stakeholders can accelerate the deployment of electric mobility solutions. These partnerships can also facilitate the transition to electric buses, which have strong support from urban respondents.
In conclusion, the path to widespread electric mobility adoption requires addressing cost, convenience, and trust challenges through coordinated efforts. By focusing on these key areas, the industry can pave the way for a more connected and sustainable mobility future.
Want insights on IoT trends delivered to your inbox? Join the 451 Alliance.

