
Source: Gail Shotlander/Stock Photos/via Getty Images.
The automotive industry is undergoing a seismic shift with the evolution of autonomous driving technology. This transformation is not just about the vehicles themselves but also the ecosystems in which they operate. With advances in IoT, AI, machine learning, connectivity and data analytics, autonomous vehicles are becoming increasingly capable. This blog post aims to explore the opportunities and challenges of autonomous driving technology adoption.
Advancing from driver assistance to complete vehicle autonomy
Autonomous driving technology has evolved significantly, transitioning from basic driver assistance systems to fully autonomous vehicles. Vehicles rely on a network of sensors, including cameras, LiDAR (light detection and ranging) and radar systems, to perceive their environment and collect data. AI algorithms process this data to identify objects and make informed decisions. High-performance computing resources, such as GPUs and TPUs, are essential for handling these computational demands and improving response times.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) International created the SAE J3016 standard, which outlines six levels of driving automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). Each level represents an increase in autonomy, with Level 5 being capable of managing all driving tasks in any situation.
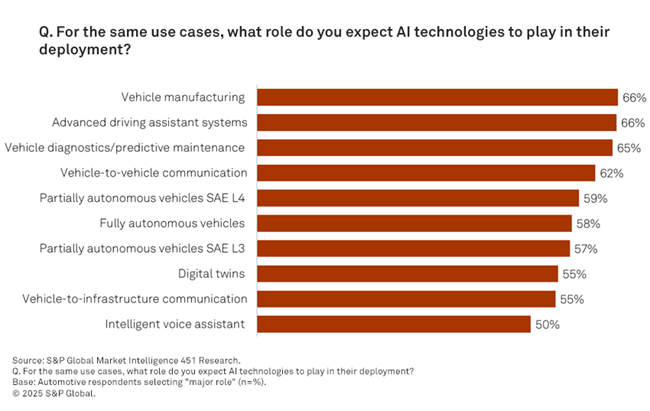
The concept of the operational design domain (ODD) is crucial in defining the specific conditions under which an autonomous vehicle can operate safely. ODD includes factors such as environmental, geographical and time-of-day conditions, as well as traffic and roadway characteristics. While AI and IoT data management are important at all levels of driver assistance and automation, their integration becomes crucial from SAE Level 3 onward. At this level, vehicles can handle most driving tasks but still require human intervention in certain situations. Therefore, advanced technologies are key for making complex decisions and managing dynamic driving environments independently, ensuring higher levels of autonomy and safety. According to a recent survey conducted by S&P Global Market Intelligence 451 Research, automotive organizations expect that AI will play a major role in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) (including SAE Level 1 and 2), Level 3, 4 and fully autonomous vehicles compared with other IoT use cases.
Challenges in adoption
Despite the momentum toward fully autonomous vehicles, several challenges remain. Scalability, high costs, adaptability, regulatory hurdles and consumer acceptance are significant obstacles. Also, according to 451 Research, while ADAS features are widely accepted, consumer preference decreases as the level of automation increases. Only 13% of customers prefer SAE Levels 4 and 5, which include mobility as a service and robotaxis.
Regulatory frameworks are emerging globally, with the US, EU, the UK, UAE, Japan and South Korea developing guidelines to support autonomous vehicle deployment. These frameworks aim to modernize regulations and prepare transportation systems for autonomous technologies.
Opportunity for digital infrastructure providers
The transition to advanced autonomous vehicle technologies opens up new opportunities for digital infrastructure providers. Collaborations between autonomous driving companies and hyperscalers are crucial for leveraging supercomputing technologies to enhance AI capabilities and scale deep-learning models. Digital infrastructure providers can aid in scaling architectures, facilitating cloud-edge data collection and accelerating time to market.
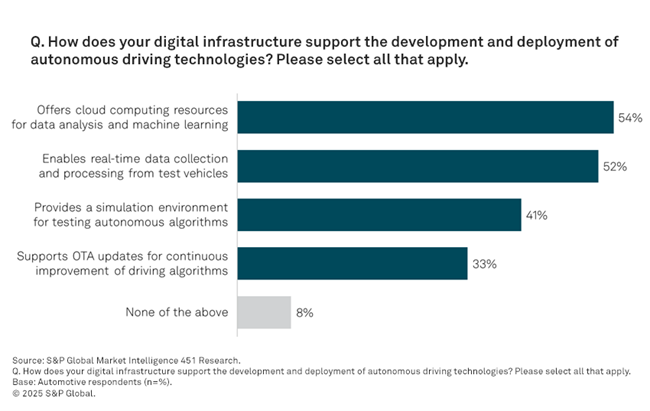
According to 451 Research, the majority of automotive organizations report that their digital infrastructure supports the development and deployment of autonomous driving technologies. Key contributions include cloud computing resources for data analysis and machine learning, real-time data collection and processing from test vehicles, and simulation environments for testing autonomous algorithms.
Future trends in autonomous vehicle technology
The future of autonomous vehicle technology lies in the transition to end-to-end autonomous vehicles, also known as AV 2.0, which integrates functions into a unified system using advanced AI models. This approach enhances scalability and adaptability, allowing systems to generalize their driving intelligence to new environments with minimal additional training. The market is competitive, with key players like Tesla Inc., Waymo and NVIDIA Corp. advancing technologies for robotaxis and mobility services. As regulations evolve and consumer acceptance grows, autonomous vehicles will likely become an integral part of our transportation systems, offering new opportunities and challenges for organizations worldwide.
Want insights on consumer technology trends delivered to your inbox? Join the 451 Alliance.
This content may be AI-assisted and is composed, reviewed, edited and approved by S&P Global in accordance with our Terms of Service.

